Gum Disease Treatment in Channapatna
- 2 months ago
- Gum Disease Treatment in Channapatna ,
- Wisdom teeth removal treatment in channapatana ,
- Dental Implants Treatment Channapatana ,
- Teeth Whitening Treatment At Channapatana ,
- ROOT CANAL TREATMENT ,
- Teeth Replacement in Channapatna
Contact : +919901344447
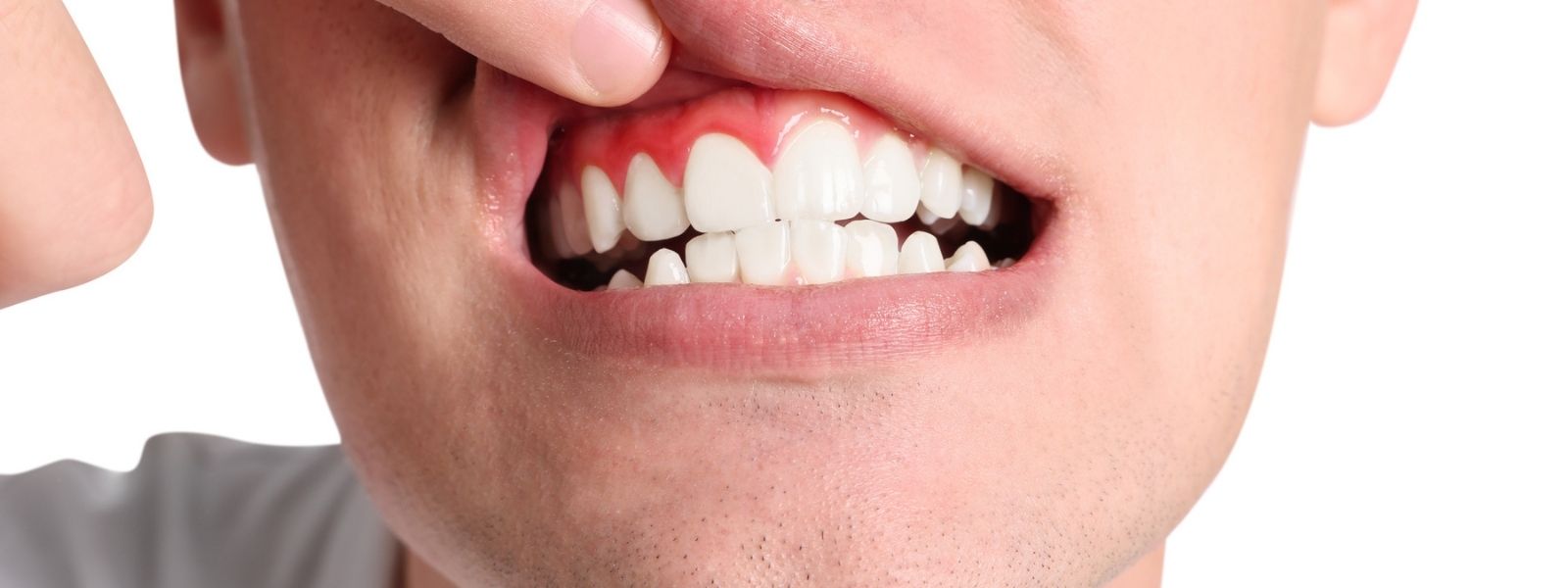
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a serious oral health condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It is primarily caused by the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, on the teeth and gums. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss and even contribute to other health problems such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Fortunately, gum disease is preventable and treatable, especially when caught early.
Types of Gum Disease
There are two main stages of gum disease:
-
Gingivitis: This is the early stage of gum disease, characterized by redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums. Gingivitis is caused by the buildup of plaque and can be reversed with proper oral hygiene and professional dental cleaning.
-
Periodontitis: If gingivitis is not treated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease. Periodontitis involves inflammation and infection of the gums, which can cause damage to the tissues and bones that support the teeth. In advanced cases, teeth may become loose and fall out or require extraction.
Causes of Gum Disease
Gum disease is primarily caused by poor oral hygiene, which leads to the accumulation of plaque and tartar on the teeth. Other factors that can contribute to gum disease include:
- Smoking or using tobacco
- Hormonal changes (e.g., pregnancy, menopause)
- Certain medications that reduce saliva production
- Genetic predisposition
- Diabetes
- Poor nutrition
- Stress
- Immune system disorders
Symptoms of Gum Disease
The symptoms of gum disease vary depending on its stage, but common signs include:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
- Receding gums (teeth appearing longer)
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Pus between the teeth and gums
- Painful chewing
Treatment for Gum Disease
The treatment for gum disease depends on its severity. Early intervention can prevent the progression of the disease and help maintain good oral health.
-
Non-surgical treatments:
-
Professional cleaning: In the early stages of gum disease (gingivitis), a thorough dental cleaning by a hygienist can remove plaque and tartar from above and below the gumline. Regular cleanings every six months are essential to prevent the recurrence of gum disease.
-
Scaling and root planing: This deep-cleaning procedure is recommended for patients with periodontitis. Scaling removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline, while root planing smooths the tooth roots to help the gums reattach to the teeth. This procedure may require local anesthesia and multiple visits.
-
-
Surgical treatments:
-
Flap surgery: If the gum disease has progressed to an advanced stage, flap surgery may be necessary. This involves lifting the gums to remove tartar deep below the gumline and then stitching the gums back in place to reduce pockets where bacteria can accumulate.
-
Bone grafts: In cases where the bone supporting the teeth has been destroyed, bone grafts can be used to regenerate lost bone. The new bone tissue helps stabilize the teeth and promotes healing.
-
Soft tissue grafts: Gum recession may require soft tissue grafts to cover exposed roots and prevent further damage.
-
Guided tissue regeneration: This procedure stimulates the growth of bone and gum tissue in areas where they have been destroyed by periodontal disease.
-
-
Medications:
- Antibiotics, either topical or oral, may be prescribed to control bacterial infection.
- Antiseptic mouthwashes can be recommended to reduce bacteria in the mouth and aid in healing.
Preventing Gum Disease
The best way to prevent gum disease is by maintaining good oral hygiene. This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and check-ups. A balanced diet and avoiding smoking or tobacco use also play a critical role in gum disease prevention. If you notice any signs of gum disease, such as bleeding gums or persistent bad breath, it’s essential to seek dental care promptly.
Early detection and treatment of gum disease can prevent serious complications and help maintain a healthy, beautiful smile.
